Filters: Tags: pinus edulis (X)
25 results (60ms)|
Filters
Contacts
(Less)
|
Fire is known to structure tree populations, but the role of broad-scale climate variability is less clear. For example, the influence of climatic ?teleconnections? (the relationship between oceanic?atmospheric fluctuations and anomalous weather patterns across broad scales) on forest age structure is relatively unexplored. We sampled semiarid pi�on?juniper (Pinus edulis?Juniperus osteosperma) woodlands in western Colorado, USA, to test the hypothesis that woodland age structures are shaped by climate, including links to oceanic?atmospheric fluctuations, and by past fires and livestock grazing. Low-severity surface fire was lacking, as fire scars were absent, and did not influence woodland densities, but stand-replacing...
• Theoretical and empirical research has supported the hypothesis that plant–plant interactions change from competition to facilitation with increasing abiotic stress. However, the consistency of such changes has been questioned in arid and semiarid ecosystems. • During a drought in the semiarid south-western USA, we used observations and a field experiment to examine the interactions between juveniles of a foundation tree (Pinyon pine, Pinus edulis ) and a common shrub (Apache plume, Fallugia paradoxa ) in replicated areas of high and low stress. • The presence of F. paradoxa reduced P. edulis performance at low-stress sites, but had the opposite effect at high-stress sites. However, the intensity of the...
Categories: Publication;
Types: Citation,
Journal Citation;
Tags: New Phytologist,
Pinus edulis,
climate change,
competition,
environmental stress,

This digital range map represents the range of Colorado pinyon pine (Pinus edulis) in western North America. Data from multiple sources, including existing digitized maps, tabular data, personal communications, USDA Forest Service Inventory and Analysis data, and figures from other publications, were synthesized to create a single digital distribution. The distribution was peer reviewed and iteratively revised based on personal observations of regional authorities.
Fire is known to structure tree populations, but the role of broad-scale climate variability is less clear. For example, the influence of climatic ?teleconnections? (the relationship between oceanic?atmospheric fluctuations and anomalous weather patterns across broad scales) on forest age structure is relatively unexplored. We sampled semiarid pi�on?juniper (Pinus edulis?Juniperus osteosperma) woodlands in western Colorado, USA, to test the hypothesis that woodland age structures are shaped by climate, including links to oceanic?atmospheric fluctuations, and by past fires and livestock grazing. Low-severity surface fire was lacking, as fire scars were absent, and did not influence woodland densities, but stand-replacing...
These data were compiled to evaluate pinyon-juniper regeneration dynamics following stand-replacing wildfire and thinning treatments. Objectives of our study were to investigate vegetation community composition and tree recruitment in post-fire and post-thinning environments. These data represent plant and biological soil crust community composition and climatological records among intact, thinned, and burned pinyon–juniper woodlands. These data were collected in Mesa Verde National Park and Ute Mountain Ute Tribal Park from 6/1/2021 to 6/10/2021 and from 03/1/2022 to 11/30/2022 at two burned and two intact pinyon-juniper ecosystems in Mesa Verde National Park only. These data were collected by the U.S. Geological...
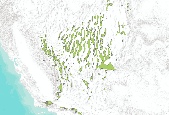
This data set represent the digital range map of Single-Needle Pinyon Pine (Pinus monophylla) in western North America. Data from multiple sources, including existing digitized maps, tabular data, personal communication, and figures from other publications, were synthesized to create a single digital distribution. The distribution was peer reviewed and iteratively revised based on personal observations of regional authorities.
Belowground interactions can affect plants either directly or indirectly via their associated mycorrhizal fungi. However, few studies have experimentally examined the consequences of interspecific root interactions for these important mutualists in the field. We used a trenching experiment to examine how belowground interactions between pinyon pine and one-seed juniper affected the ectomycorrhizal (EM) fungal communities of pinyon pine. Three major findings emerged: (1) pinyons responded to the reduction of juniper roots with a near doubling of fine root biomass in just two years, (2) this increase in pinyon roots translated into a potential two-fold increase in EM abundance, and (3) the EM fungal communities of...
Categories: Publication;
Types: Citation,
Journal Citation;
Tags: Arizona (USA) pinyon-juniper woodland,
Ecological Society of America,
Ecology,
Juniperus monosperma,
Pinus edulis,
1 Although drought frequency and severity are predicted to increase across numerous continental interiors, the consequences of these changes for dominant plants are largely unknown. Over the last decade, the south-western US has experienced six drought years, including the extreme droughts of 1996 and 2002, which led to widespread tree mortality across northern Arizona. 2 We examined the impact of these droughts on the co-dominant tree species of the pinyon?juniper woodland (Pinus edulis and Juniperus monosperma), a major vegetation type in the US. 3 Pinyon mortality following both droughts was 6.5-fold higher than juniper mortality. In addition, large pinyons suffered 2?6-fold greater mortality than small pinyons,...
Categories: Publication;
Types: Citation,
Journal Citation;
Tags: Journal of Ecology,
Juniperus monosperma,
Pinus edulis,
climate change,
differential mortality,
Stomatal closure during periods of moisture deficiency should theoretically lead to elevated 13C/12C ratios as reduction of available CO2 leads to diminished photosynthetic discrimination against 13C in favor of 12C. Stable-carbon isotope ratio chronologies developed from 5-yr tree-ring groups at 17 sites in six southwestern states were tested for a drought relationship by first fitting a spline curve to each chronology to remove the long-term trend and calculating indices as the ratio of actual to spline curve value. The time series of ?Del Indices? so developed are significantly correlated with 5-yr mean Palmer Hydrological Drought Indices (post-1930 period) and reconstructed July Palmer Drought Severity Indices...
Categories: Publication;
Types: Citation,
Journal Citation;
Tags: C-13/C-12,
Journal of the American Water Resources Association,
Palmer Drought Indices,
Pinus edulis,
Southwest,
These data were compiled to help understand how climate change may impact dryland pinyon-juniper ecosystems in coming decades, and how resource management might be able to minimize those impacts. Objective(s) of our study were to model the demographic rates of PJ woodlands to estimate the areas that may decline in the future vs. those that will be stable. We quantified populations growth rates across broad geographic areas, and identified the relative roles of recruitment and mortality in driving potential future changes in population viability in 5 tree species that are major components of these dry forests. We used this demographic model to project pinyon-juniper population stability under future climate conditions,...
In water-limited environments of the intermountain region of North America, summer precipitation may play a role in the structure and function of aridland communities and ecosystems. This study examined the potential reliance on summer precipitation of two widespread, coexisting woody species in the southwestern United States, Pinus edulis Englmn. (Colorado piñon) and Juniperus osteosperma (Torr) Little (Utah juniper). The current distributions of P. edulis and J. osteosperma are highly suggestive of different dependencies on summer rainfall. We hypothesized that P. edulis was dependent on summer precipitation, utilizing summer precipitation even during extremely dry summers, whereas J. osteosperma was not dependent,...
Categories: Publication;
Types: Citation,
Journal Citation;
Tags: Juniperus osteosperma,
Oecologia,
Pinus edulis,
Springer Berlin / Heidelberg,
Summer precipitation,
Ectomycorrhizal abundance and community composition shifts with drought: Predictions from tree rings
Mycorrhizae play a key role in ecosystem dynamics, and it is important to understand how environmental stress and climate change affect these symbionts. Several climate models predict that the intercontinental western United States will experience an increase in extreme precipitation events and warming temperatures. In 1996, northern Arizona, USA, experienced a 100-year drought that caused high local mortality of pinyon pine (Pinus edulis), a dominant tree of the southwest. We compared trunk growth, water potentials, and ectomycorrhizal dynamics for surviving trees at three high-mortality sites and adjacent low-mortality sites. Four major patterns emerged. First, surviving trees at sites that suffered high mortality...
Categories: Publication;
Types: Citation,
Journal Citation;
Tags: Arizona,
Ecology,
Pinus edulis,
USA (northern),
climate-change effects,
Aim The geographical extent and climatic tolerances of one- and two-needled pinyon pines (Pinus subsect. Cembroides) are the focus of questions in taxonomy, palaeoclimatology and modelling of future distributions. The identification of these pines, traditionally classified by one- versus two-needled fascicles, is complicated by populations with both one- and two-needled fascicles on the same tree, and the description of two more recently described one-needled varieties: the fallax-type and californiarum-type. Because previous studies have suggested correlations between needle anatomy and climate, including anatomical plasticity reflecting annual precipitation, we approached this study at the level of the anatomy...
Categories: Publication;
Types: Citation,
Journal Citation;
Tags: Climate modelling,
Journal of Biogeography,
Pinus edulis,
Pinus monophylla,
needle anatomy,
The amount of carbon plants allocate to mycorrhizal symbionts exceeds that emitted by human activity annually. Senescent ectomycorrhizal roots represent a large input of carbon into soils, but their fate remains unknown. Here, we present the surprising result that, despite much higher nitrogen concentrations, roots colonized by ectomycorrhizal (EM) fungi lost only one-third as much carbon as non-mycorrhizal roots after 2 years of decomposition in a piñon pine (Pinus edulis) woodland. Experimentally excluding live mycorrhizal hyphae from litter, we found that live mycorrhizal hyphae may alter nitrogen dynamics, but the afterlife (litter-mediated) effects of EM fungi outweigh the influences of live fungi on root...
Categories: Publication;
Types: Citation,
Journal Citation;
Tags: 15N,
Decomposition,
Ecology Letters,
Pinus edulis,
ectomycorrhizal roots,
In water-limited environments of the intermountain region of North America, summer precipitation may play a role in the structure and function of aridland communities and ecosystems. This study examined the potential reliance on summer precipitation of two widespread, coexisting woody species in the southwestern United States, Pinus edulis Englmn. (Colorado pi�on) and Juniperus osteosperma (Torr) Little (Utah juniper). The current distributions of P. edulis and J. osteosperma are highly suggestive of different dependencies on summer rainfall. We hypothesized that P. edulis was dependent on summer precipitation, utilizing summer precipitation even during extremely dry summers, whereas J. osteosperma was not dependent,...
Categories: Publication;
Types: Citation,
Journal Citation;
Tags: Juniperus osteosperma,
Oecologia,
Pinus edulis,
Springer Berlin / Heidelberg,
Summer precipitation,
Regional, high-resolution mapping of vegetation cover and biomass is central to understanding changes to the terrestrial carbon (C) cycle, especially in the context of C management. The third most extensive vegetation type in the United States is pinyon-juniper (P-J) woodland, yet the spatial patterns of tree cover and aboveground biomass (AGB) of P-J systems are poorly quantified. We developed a synoptic remote-sensing approach to scale up pinyon and juniper projected cover (hereafter "cover") and AGB field observations from plot to regional levels using fractional photosynthetic vegetation (PV) cover derived from airborne imaging spectroscopy and Landsat satellite data. Our results demonstrated strong correlations...
Categories: Publication;
Types: Citation,
Journal Citation;
Tags: AVIRIS,
ETM+,
Ecological Applications,
Ecological Society of America,
Juniperus osteosperma,
Herbivore alteration of litter inputs may change litter decomposition rates and influence ecosystem nutrient cycling. In a semiarid woodland at Sunset Crater National Monument, Arizona, long-term insect herbivore removal experiments and the presence of herbivore resistant and susceptible pinyon pines (Pinus edulis) have allowed characterization of the population- and community-level effects of herbivory. Here we report how these same two herbivores, the mesophyll-feeding scale insect Matsucoccus acalyptus and the stem-boring moth Dioryctria albovittella alter litter quality, dynamics, and decomposition in this ecosystem. We measured aboveground litterfall, litter chemical composition, and first-year litter decomposition...
Categories: Publication;
Types: Citation,
Journal Citation;
Tags: Arizona,
Dioryctria albovittella,
Ecology,
Matsucoccus acalyptus,
Pinus edulis,
Fire is known to structure tree populations, but the role of broad-scale climate variability is less clear. For example, the influence of climatic “teleconnections” (the relationship between oceanic–atmospheric fluctuations and anomalous weather patterns across broad scales) on forest age structure is relatively unexplored. We sampled semiarid piñon–juniper (Pinus edulis–Juniperus osteosperma) woodlands in western Colorado, USA, to test the hypothesis that woodland age structures are shaped by climate, including links to oceanic–atmospheric fluctuations, and by past fires and livestock grazing. Low-severity surface fire was lacking, as fire scars were absent, and did not influence woodland densities, but stand-replacing...
In the arid southwest of North America, winter precipitation penetrates to deep soil layers, whereas summer "monsoon" precipitation generally wets only surface layers. Use of these spatially separated water sources was determined for three dominant tree species of the pinyon-juniper ecosystem at six sites along a gradient of increasing summer precipitation in Utah and Arizona. Mean summer precipitation ranged from 79 to 286 mm, or from 18% to 60% of the annual total across the gradient. We predicted that, along this summer rainfall gradient, populations of dominant tree species would exhibit a clinal off-on response for use of water from upper soil layers, responding at particular threshold levels of summer precipitation...
Categories: Publication;
Types: Citation,
Journal Citation;
Tags: D/H Ratios,
Ecological Monographs,
Ecological Society of America,
Juniperus osteosperma,
Pinus edulis,
The fine roots of trees are concentrated on lateral branches that arise from perennial roots. They are important in the acquisition of water and essential nutrients, and at the ecosystem level, they make a significant contribution to biogeochemical cycling. Fine roots have often been studied according to arbitrary size classes, e.g., all roots less than 1 or 2 mm in diameter. Because of the size class approach, the position of an individual root on the complex lateral branching system has often been ignored, and relationships between the form of the branching root system and its function are poorly understood. The fine roots of both gymnosperms and angiosperms, which formed ectomycorrhizae (EM) and arbuscular mycorrhizae...
Categories: Publication;
Types: Citation,
Journal Citation;
Tags: Acer saccharum,
Ecological Monographs,
Juniperus monosperma,
Liriodendron tulipifera,
Picea glauca,
|

|