Filters: Tags: VEMAP (X)
31 results (15ms)|
Filters
Date Range
Contacts Tag Types Tag Schemes |

Two future climate change scenarios at a resolution of 0.5 degree latitude/longitude for the conterminous United States were used in the Vegetation Ecosystems Modelling Analysis Project (VEMAP): a moderately warm scenario produced by the general circulation model from the Hadley Climate Centre [Johns et al., 1997; Mitchell and Johns, 1997], HADCM2SUL (up to a 2.8oC increase in average annual U.S. temperature in 2100) and a warmer scenario (up to a 5.8oC increase in average annual U.S. temperature in 2100), CGCM1, from the Canadian Climate Center [Boer et al., 1999a, 1999b; Flato et al., 1999]. Both general circulation models (GCMs) included sulfate aerosols and a fully dynamic 3-D ocean. Both transient scenarios...

Two future climate change scenarios at a resolution of 0.5 degree latitude/longitude for the conterminous United States were used in the Vegetation Ecosystems Modelling Analysis Project (VEMAP): a moderately warm scenario produced by the general circulation model from the Hadley Climate Centre [Johns et al., 1997; Mitchell and Johns, 1997], HADCM2SUL (up to a 2.8oC increase in average annual U.S. temperature in 2100) and a warmer scenario (up to a 5.8oC increase in average annual U.S. temperature in 2100), CGCM1, from the Canadian Climate Center [Boer et al., 1999a, 1999b; Flato et al., 1999]. Both general circulation models (GCMs) included sulfate aerosols and a fully dynamic 3-D ocean. Both transient scenarios...

Two future climate change scenarios at a resolution of 0.5 degree latitude/longitude for the conterminous United States were used in the Vegetation Ecosystems Modelling Analysis Project (VEMAP): a moderately warm scenario produced by the general circulation model from the Hadley Climate Centre [Johns et al., 1997; Mitchell and Johns, 1997], HADCM2SUL (up to a 2.8oC increase in average annual U.S. temperature in 2100) and a warmer scenario (up to a 5.8oC increase in average annual U.S. temperature in 2100), CGCM1, from the Canadian Climate Center [Boer et al., 1999a, 1999b; Flato et al., 1999]. Both general circulation models (GCMs) included sulfate aerosols and a fully dynamic 3-D ocean. Both transient scenarios...

The Vegetation/Ecosystem Modeling and Analysis Project (VEMAP) was a multi-institutional, international effort that addressed the response of biogeography and biogeochemistry to environmental variability in climate and other drivers in both space and time domains. The objectives of VEMAP were to study the intercomparison of biogeochemistry models and vegetationtype distribution models (biogeography models) and determine their sensitivity to changing climate, elevated atmospheric carbon dioxide concentrations, and other sources of altered forcing. Soil properties were based on a 10-km gridded EPA soil database developed by Kern (1994, 1995). Two soil coverages are provided in the Kern data set: one from the USDA...

The Vegetation/Ecosystem Modeling and Analysis Project (VEMAP) was a multi-institutional, international effort that addressed the response of biogeography and biogeochemistry to environmental variability in climate and other drivers in both space and time domains. The objectives of VEMAP were to study the intercomparison of biogeochemistry models and vegetationtype distribution models (biogeography models) and determine their sensitivity to changing climate, elevated atmospheric carbon dioxide concentrations, and other sources of altered forcing. Soil properties were based on a 10-km gridded EPA soil database developed by Kern (1994, 1995). Two soil coverages are provided in the Kern data set: one from the USDA...

The full VEMAP dataset covers the period 1895—1993 on a 0.5° latitude/longitude grid. Climate is represented at both monthly and daily timesteps. Variables are: precipitation, mininimum and maximum temperature, total incident solar radiation, daylight-period irradiance, vapor pressure, and daylight-period relative humidity. The dataset was derived from US Historical Climate Network (HCN), cooperative net work, and snowpack telemetry (SNOTEL) monthly precipitation and mean minimum and maximum temperature station data. VEMAP participants employed techniques that rely on geostatistical and physical relation ships to create the temporally and spatially complete dataset. They developed a local kriging prediction model...
Tags: temperature,
vemap
Vegetation types from Kuchler (1975) potential vegetation map were aggregated into 35 classes as part of the VEMAP project (Vegetation/Ecosystem Modeling and Analysis Project, Kittel et al. 1995). Functional vegetation types were reclassified (grouped in ArcMap) by the Conservation Biology Institute to reflect the classification scheme used by Brendan Rogers.

The Vegetation/Ecosystem Modeling and Analysis Project (VEMAP) was a multi-institutional, international effort that addressed the response of biogeography and biogeochemistry to environmental variability in climate and other drivers in both space and time domains. The objectives of VEMAP were to study the intercomparison of biogeochemistry models and vegetationtype distribution models (biogeography models) and determine their sensitivity to changing climate, elevated atmospheric carbon dioxide concentrations, and other sources of altered forcing. Soil properties were based on a 10-km gridded EPA soil database developed by Kern (1994, 1995). Two soil coverages are provided in the Kern data set: one from the USDA...
Two future climate change scenarios at a resolution of 0.5 degree latitude/longitude for the conterminous United States were used in the Vegetation Ecosystems Modelling Analysis Project (VEMAP): a moderately warm scenario produced by the general circulation model from the Hadley Climate Centre [Johns et al., 1997; Mitchell and Johns, 1997], HADCM2SUL (up to a 2.8oC increase in average annual U.S. temperature in 2100) and a warmer scenario (up to a 5.8oC increase in average annual U.S. temperature in 2100), CGCM1, from the Canadian Climate Center [Boer et al., 1999a, 1999b; Flato et al., 1999]. Both general circulation models (GCMs) included sulfate aerosols and a fully dynamic 3-D ocean. Both transient scenarios...

The spatial resolution of this dataset is 50 km. The Vegetation/Ecosystem Modeling and Analysis Project (VEMAP) was a multi-institutional, international effort that addressed the response of biogeography and biogeochemistry to environmental variability in climate and other drivers in both space and time domains. The objectives of VEMAP were to study the intercomparison of biogeochemistry models and vegetation type distribution models (biogeography models) and determine their sensitivity to changing climate, elevated atmospheric carbon dioxide concentrations, and other sources of altered forcing. Soil properties were based on a 10-km gridded EPA soil database developed by Kern (1994, 1995). Two soil coverages are...

The spatial resolution of this dataset is 50 km. The Vegetation/Ecosystem Modeling and Analysis Project (VEMAP) was a multi-institutional, international effort that addressed the response of biogeography and biogeochemistry to environmental variability in climate and other drivers in both space and time domains. The objectives of VEMAP were to study the intercomparison of biogeochemistry models and vegetation type distribution models (biogeography models) and determine their sensitivity to changing climate, elevated atmospheric carbon dioxide concentrations, and other sources of altered forcing. Soil properties were based on a 10-km gridded EPA soil database developed by Kern (1994, 1995). Two soil coverages are...
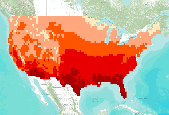
Two future climate change scenarios at a resolution of 0.5 degree latitude/longitude for the conterminous United States were used in the Vegetation Ecosystems Modelling Analysis Project (VEMAP): a moderately warm scenario produced by the general circulation model from the Hadley Climate Centre [Johns et al., 1997; Mitchell and Johns, 1997], HADCM2SUL (up to a 2.8oC increase in average annual U.S. temperature in 2100) and a warmer scenario (up to a 5.8oC increase in average annual U.S. temperature in 2100), CGCM1, from the Canadian Climate Center [Boer et al., 1999a, 1999b; Flato et al., 1999]. Both general circulation models (GCMs) included sulfate aerosols and a fully dynamic 3-D ocean. Both transient scenarios...

MC1 is a dynamic vegetation model for estimating the distribution of vegetation and associated ecosystem fluxes of carbon, nutrients, and water. It was created to assess the potential impacts of global climate change on ecosystem structure and function at a wide range of spatial scales from landscape to global. The model incorporates transient dynamics to make predictions about the patterns of ecological change. MC1 was created by combining physiologically based biogeographic rules defined in the MAPSS model with a modified version of the biogeochemical model, CENTURY. MC1 includes a fire module, MCFIRE, that mechanistically simulates the occurrence and impacts of fire events. Climate input data sources for this...

This is a mode vegetation map resulting from annual MC1 model vegetation output. It is the vegetation class that occurs with greatest frequency for the years 2070-2099. MC1 is a dynamic vegetation model for estimating the distribution of vegetation and associated ecosystem fluxes of carbon, nutrients, and water. It was created to assess the potential impacts of global climate change on ecosystem structure and function at a wide range of spatial scales from landscape to global. The model incorporates transient dynamics to make predictions about the patterns of ecological change. MC1 was created by combining physiologically based biogeographic rules defined in the MAPSS model with a modified version of the biogeochemical...

Two future climate change scenarios at a resolution of 0.5 degree latitude/longitude for the conterminous United States were used in the Vegetation Ecosystems Modelling Analysis Project (VEMAP): a moderately warm scenario produced by the general circulation model from the Hadley Climate Centre [Johns et al., 1997; Mitchell and Johns, 1997], HADCM2SUL (up to a 2.8oC increase in average annual U.S. temperature in 2100) and a warmer scenario (up to a 5.8oC increase in average annual U.S. temperature in 2100), CGCM1, from the Canadian Climate Center [Boer et al., 1999a, 1999b; Flato et al., 1999]. Both general circulation models (GCMs) included sulfate aerosols and a fully dynamic 3-D ocean. Both transient scenarios...
Two future climate change scenarios at a resolution of 0.5 degree latitude/longitude for the conterminous United States were used in the Vegetation Ecosystems Modelling Analysis Project (VEMAP): a moderately warm scenario produced by the general circulation model from the Hadley Climate Centre [Johns et al., 1997; Mitchell and Johns, 1997], HADCM2SUL (up to a 2.8oC increase in average annual U.S. temperature in 2100) and a warmer scenario (up to a 5.8oC increase in average annual U.S. temperature in 2100), CGCM1, from the Canadian Climate Center [Boer et al., 1999a, 1999b; Flato et al., 1999]. Both general circulation models (GCMs) included sulfate aerosols and a fully dynamic 3-D ocean. Both transient scenarios...

Two future climate change scenarios at a resolution of 0.5 degree latitude/longitude for the conterminous United States were used in the Vegetation Ecosystems Modelling Analysis Project (VEMAP): a moderately warm scenario produced by the general circulation model from the Hadley Climate Centre [Johns et al., 1997; Mitchell and Johns, 1997], HADCM2SUL (up to a 2.8oC increase in average annual U.S. temperature in 2100) and a warmer scenario (up to a 5.8oC increase in average annual U.S. temperature in 2100), CGCM1, from the Canadian Climate Center [Boer et al., 1999a, 1999b; Flato et al., 1999]. Both general circulation models (GCMs) included sulfate aerosols and a fully dynamic 3-D ocean. Both transient scenarios...

The Vegetation/Ecosystem Modeling and Analysis Project (VEMAP) was a multi-institutional, international effort that addressed the response of biogeography and biogeochemistry to environmental variability in climate and other drivers in both space and time domains. The objectives of VEMAP were to study the intercomparison of biogeochemistry models and vegetationtype distribution models (biogeography models) and determine their sensitivity to changing climate, elevated atmospheric carbon dioxide concentrations, and other sources of altered forcing. Soil properties were based on a 10-km gridded EPA soil database developed by Kern (1994, 1995). Two soil coverages are provided in the Kern data set: one from the USDA...

The Vegetation/Ecosystem Modeling and Analysis Project (VEMAP) was a multi-institutional, international effort that addressed the response of biogeography and biogeochemistry to environmental variability in climate and other drivers in both space and time domains. The objectives of VEMAP were to study the intercomparison of biogeochemistry models and vegetationtype distribution models (biogeography models) and determine their sensitivity to changing climate, elevated atmospheric carbon dioxide concentrations, and other sources of altered forcing. Soil properties were based on a 10-km gridded EPA soil database developed by Kern (1994, 1995). Two soil coverages are provided in the Kern data set: one from the USDA...

Two future climate change scenarios at a resolution of 0.5 degree latitude/longitude for the conterminous United States were used in the Vegetation Ecosystems Modelling Analysis Project (VEMAP): a moderately warm scenario produced by the general circulation model from the Hadley Climate Centre [Johns et al., 1997; Mitchell and Johns, 1997], HADCM2SUL (up to a 2.8oC increase in average annual U.S. temperature in 2100) and a warmer scenario (up to a 5.8oC increase in average annual U.S. temperature in 2100), CGCM1, from the Canadian Climate Center [Boer et al., 1999a, 1999b; Flato et al., 1999]. Both general circulation models (GCMs) included sulfate aerosols and a fully dynamic 3-D ocean. Both transient scenarios...
|

|