Filters: Tags: tree mortality (X)
372 results (36ms)|
Filters
Date Range
Extensions Types Contacts
Categories Tag Types
|
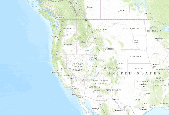
Western Conterminous US Killed Trees Per Grid Cell, IPS Engraver Beetles, No Data on Host Type, 2001
This is one of many datasets generated as part of the cited study. It shows Western Conterminous US Killed Trees Per Grid Cell, IPS Engraver Beetles, No Data on Host Type, 2001. Below is a description of the entire study: Abstract. Outbreaks of aggressive bark beetle species cause widespread tree mortality, affecting timber production, wildlife habitat, wildfire, forest composition and structure, biogeochemical cycling, and biogeophysical processes. As a result, agencies responsible for forest management in the United States and British Columbia conduct aerial surveys to map these forest disturbances. Here we combined aerial surveys from British Columbia (2001â2010) and the western conterminous United States...

This is one of many datasets generated as part of the cited study. It shows British Columbia percent mortality area (0-100% of the gridcell area containing killed trees) due to Western Balsam Bark Beetle, 2009. Below is a description of the entire study: Abstract. Outbreaks of aggressive bark beetle species cause widespread tree mortality, affecting timber production, wildlife habitat, wildfire, forest composition and structure, biogeochemical cycling, and biogeophysical processes. As a result, agencies responsible for forest management in the United States and British Columbia conduct aerial surveys to map these forest disturbances. Here we combined aerial surveys from British Columbia (2001–2010) and the western...
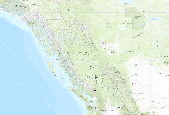
This is one of many datasets generated as part of the cited study. It shows British Columbia percent mortality area (0-100% of the gridcell area containing killed trees) due to Douglas-Fir Beetle, 2009. Below is a description of the entire study: Abstract. Outbreaks of aggressive bark beetle species cause widespread tree mortality, affecting timber production, wildlife habitat, wildfire, forest composition and structure, biogeochemical cycling, and biogeophysical processes. As a result, agencies responsible for forest management in the United States and British Columbia conduct aerial surveys to map these forest disturbances. Here we combined aerial surveys from British Columbia (2001–2010) and the western conterminous...

This is one of many datasets generated as part of the cited study. It shows British Columbia percent mortality area (0-100% of the gridcell area containing killed trees) due to Western Balsam Bark Beetle, 2005. Below is a description of the entire study: Abstract. Outbreaks of aggressive bark beetle species cause widespread tree mortality, affecting timber production, wildlife habitat, wildfire, forest composition and structure, biogeochemical cycling, and biogeophysical processes. As a result, agencies responsible for forest management in the United States and British Columbia conduct aerial surveys to map these forest disturbances. Here we combined aerial surveys from British Columbia (2001–2010) and the western...

This is one of many datasets generated as part of the cited study. It shows British Columbia percent mortality area (0-100% of the gridcell area containing killed trees) due to Douglas-Fir Beetle, 2005. Below is a description of the entire study: Abstract. Outbreaks of aggressive bark beetle species cause widespread tree mortality, affecting timber production, wildlife habitat, wildfire, forest composition and structure, biogeochemical cycling, and biogeophysical processes. As a result, agencies responsible for forest management in the United States and British Columbia conduct aerial surveys to map these forest disturbances. Here we combined aerial surveys from British Columbia (2001–2010) and the western conterminous...

This is one of many datasets generated as part of the cited study. It shows British Columbia percent mortality area (0-100% of the gridcell area containing killed trees) due to Spruce Beetles, 2001. Below is a description of the entire study: Abstract. Outbreaks of aggressive bark beetle species cause widespread tree mortality, affecting timber production, wildlife habitat, wildfire, forest composition and structure, biogeochemical cycling, and biogeophysical processes. As a result, agencies responsible for forest management in the United States and British Columbia conduct aerial surveys to map these forest disturbances. Here we combined aerial surveys from British Columbia (2001–2010) and the western conterminous...

This is one of many datasets generated as part of the cited study. It shows British Columbia percent mortality area (0-100% of the gridcell area containing killed trees) due to Douglas-Fir Beetle, 2001. Below is a description of the entire study: Abstract. Outbreaks of aggressive bark beetle species cause widespread tree mortality, affecting timber production, wildlife habitat, wildfire, forest composition and structure, biogeochemical cycling, and biogeophysical processes. As a result, agencies responsible for forest management in the United States and British Columbia conduct aerial surveys to map these forest disturbances. Here we combined aerial surveys from British Columbia (2001–2010) and the western conterminous...
2010 USDA Forest Service, Rocky Mountain Region Aerial Detection Survey Data. This data depicts the occurrence and location of forest insect, disease, and other biotic and abiotic causes of tree mortality and tree damage. Aerial survey data is collected by observing areas of tree damage or tree mortality from an aircraft and manually recording the information onto a map. Due to the nature of aerial surveys, this data will only provide rough estimates of location, intensity and the resulting trend information for agents detectable from the air. Many of the most destructive diseases are not represented in the data because these agents are not detectable from aerial surveys. The data presented should only be used as...

This is one of many datasets generated as part of the cited study. It shows Western Conterminous US Killed Trees Per Grid Cell, Western Pine Beetle, No Data on Host Type, 2001. Below is a description of the entire study: Abstract. Outbreaks of aggressive bark beetle species cause widespread tree mortality, affecting timber production, wildlife habitat, wildfire, forest composition and structure, biogeochemical cycling, and biogeophysical processes. As a result, agencies responsible for forest management in the United States and British Columbia conduct aerial surveys to map these forest disturbances. Here we combined aerial surveys from British Columbia (2001â2010) and the western conterminous United States...

This is one of many datasets generated as part of the cited study. It shows British Columbia percent mortality area (0-100% of the gridcell area containing killed trees) due to Mountain Pine Beetle, 2009. Below is a description of the entire study: Abstract. Outbreaks of aggressive bark beetle species cause widespread tree mortality, affecting timber production, wildlife habitat, wildfire, forest composition and structure, biogeochemical cycling, and biogeophysical processes. As a result, agencies responsible for forest management in the United States and British Columbia conduct aerial surveys to map these forest disturbances. Here we combined aerial surveys from British Columbia (2001–2010) and the western...

This is one of many datasets generated as part of the cited study. It shows Western Conterminous US Killed Trees Per Grid Cell, Western Pine Beetle, No Data on Host Type, 1999. Below is a description of the entire study: Abstract. Outbreaks of aggressive bark beetle species cause widespread tree mortality, affecting timber production, wildlife habitat, wildfire, forest composition and structure, biogeochemical cycling, and biogeophysical processes. As a result, agencies responsible for forest management in the United States and British Columbia conduct aerial surveys to map these forest disturbances. Here we combined aerial surveys from British Columbia (2001â2010) and the western conterminous United States...

This is one of many datasets generated as part of the cited study. It shows Western Conterminous US Killed Trees Per Grid Cell, Western Pine Beetle, No Data on Host Type, 1997. Below is a description of the entire study: Abstract. Outbreaks of aggressive bark beetle species cause widespread tree mortality, affecting timber production, wildlife habitat, wildfire, forest composition and structure, biogeochemical cycling, and biogeophysical processes. As a result, agencies responsible for forest management in the United States and British Columbia conduct aerial surveys to map these forest disturbances. Here we combined aerial surveys from British Columbia (2001â2010) and the western conterminous United States...

This is one of many datasets generated as part of the cited study. It shows Western Conterminous US Killed Trees Per Grid Cell, Roundheaded Pine Beetle, Ponderosa Pine, 2009. Below is a description of the entire study: Abstract. Outbreaks of aggressive bark beetle species cause widespread tree mortality, affecting timber production, wildlife habitat, wildfire, forest composition and structure, biogeochemical cycling, and biogeophysical processes. As a result, agencies responsible for forest management in the United States and British Columbia conduct aerial surveys to map these forest disturbances. Here we combined aerial surveys from British Columbia (2001â2010) and the western conterminous United States...

This is one of many datasets generated as part of the cited study. It shows Western Conterminous US Killed Trees Per Grid Cell, Western Pine Beetle, No Data on Host Type, 2008. Below is a description of the entire study: Abstract. Outbreaks of aggressive bark beetle species cause widespread tree mortality, affecting timber production, wildlife habitat, wildfire, forest composition and structure, biogeochemical cycling, and biogeophysical processes. As a result, agencies responsible for forest management in the United States and British Columbia conduct aerial surveys to map these forest disturbances. Here we combined aerial surveys from British Columbia (2001â2010) and the western conterminous United States...

This is one of many datasets generated as part of the cited study. It shows Western Conterminous US Killed Trees Per Grid Cell, Western Balsam Bark Beetle, Subalpine Fir, 2008. Below is a description of the entire study: Abstract. Outbreaks of aggressive bark beetle species cause widespread tree mortality, affecting timber production, wildlife habitat, wildfire, forest composition and structure, biogeochemical cycling, and biogeophysical processes. As a result, agencies responsible for forest management in the United States and British Columbia conduct aerial surveys to map these forest disturbances. Here we combined aerial surveys from British Columbia (2001â2010) and the western conterminous United States...

This is one of many datasets generated as part of the cited study. It shows Western Conterminous US Killed Trees Per Grid Cell, Western Balsam Bark Beetle, No Data on Host Type, 2008. Below is a description of the entire study: Abstract. Outbreaks of aggressive bark beetle species cause widespread tree mortality, affecting timber production, wildlife habitat, wildfire, forest composition and structure, biogeochemical cycling, and biogeophysical processes. As a result, agencies responsible for forest management in the United States and British Columbia conduct aerial surveys to map these forest disturbances. Here we combined aerial surveys from British Columbia (2001â2010) and the western conterminous United...

This is one of many datasets generated as part of the cited study. It shows Western Conterminous US Killed Trees Per Grid Cell, Mountain Pine Beetle, Bristlecone Pine, 2007. Below is a description of the entire study: Abstract. Outbreaks of aggressive bark beetle species cause widespread tree mortality, affecting timber production, wildlife habitat, wildfire, forest composition and structure, biogeochemical cycling, and biogeophysical processes. As a result, agencies responsible for forest management in the United States and British Columbia conduct aerial surveys to map these forest disturbances. Here we combined aerial surveys from British Columbia (2001â2010) and the western conterminous United States (1997â2010),...

This is one of many datasets generated as part of the cited study. It shows Western Conterminous US Killed Trees Per Grid Cell, Mountain Pine Beetle, Western White Pine, 2005. Below is a description of the entire study: Abstract. Outbreaks of aggressive bark beetle species cause widespread tree mortality, affecting timber production, wildlife habitat, wildfire, forest composition and structure, biogeochemical cycling, and biogeophysical processes. As a result, agencies responsible for forest management in the United States and British Columbia conduct aerial surveys to map these forest disturbances. Here we combined aerial surveys from British Columbia (2001â2010) and the western conterminous United States...

This is one of many datasets generated as part of the cited study. It shows Western Conterminous US Killed Trees Per Grid Cell, Mountain Pine Beetle, Bristlecone Pine, 2004. Below is a description of the entire study: Abstract. Outbreaks of aggressive bark beetle species cause widespread tree mortality, affecting timber production, wildlife habitat, wildfire, forest composition and structure, biogeochemical cycling, and biogeophysical processes. As a result, agencies responsible for forest management in the United States and British Columbia conduct aerial surveys to map these forest disturbances. Here we combined aerial surveys from British Columbia (2001â2010) and the western conterminous United States (1997â2010),...

This is one of many datasets generated as part of the cited study. It shows Western Conterminous US Killed Trees Per Grid Cell, Mountain Pine Beetle, Western White Pine, 2002. Below is a description of the entire study: Abstract. Outbreaks of aggressive bark beetle species cause widespread tree mortality, affecting timber production, wildlife habitat, wildfire, forest composition and structure, biogeochemical cycling, and biogeophysical processes. As a result, agencies responsible for forest management in the United States and British Columbia conduct aerial surveys to map these forest disturbances. Here we combined aerial surveys from British Columbia (2001â2010) and the western conterminous United States...
|

|